Introduction
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have become indispensable tools across various industries, from aerial photography to agriculture and beyond. Behind their sleek exteriors lie intricate systems comprised of numerous components, each playing a crucial role in ensuring the UAV’s functionality and performance. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at the key components that make up UAVs, shedding light on the inner workings of these remarkable flying machines.
Frame and Body
At the heart of every UAV is its frame and body, which serve as the structural foundation for the entire aircraft. Frames are typically constructed from lightweight materials such as carbon fiber or aluminum to maximize strength while minimizing weight. The design of the frame can vary depending on the UAV’s intended use, ranging from compact quadcopters for aerial photography to fixed-wing aircraft for long-range surveillance missions.
Propulsion System
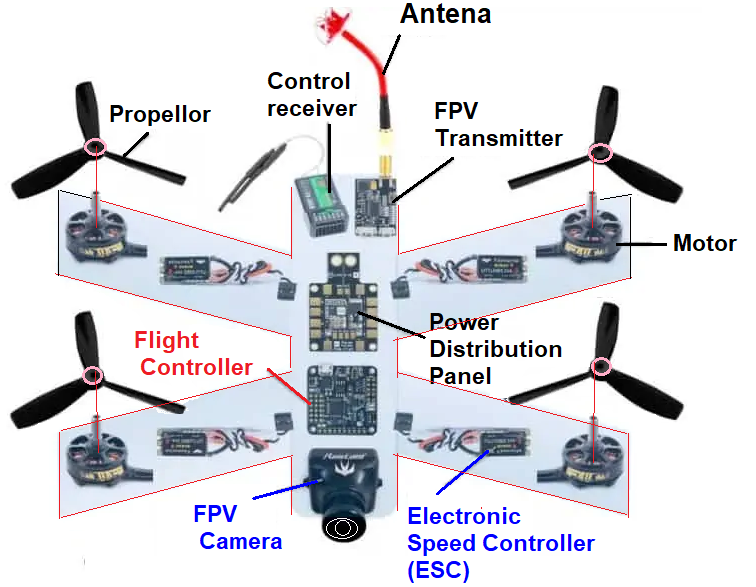
The propulsion system of a UAV consists of motors, propellers, and electronic speed controllers (ESCs) that work together to generate thrust and control the aircraft’s movement. Electric motors are commonly used in UAVs due to their efficiency and reliability. The number and configuration of motors and propellers can vary based on the UAV’s design, with quadcopters, hexacopters, and octocopters being among the most common configurations.
Flight Control System
The flight control system is the brain of the UAV, responsible for stabilizing the aircraft, controlling its orientation, and executing flight commands. It comprises a flight controller, sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and magnetometers), and software algorithms that process sensor data and adjust motor speeds to maintain stability and control. Advanced UAVs may also feature GPS receivers for autonomous navigation and position hold capabilities.
Power Source
Powering the UAV’s propulsion system and onboard electronics is a crucial component – the power source. Most UAVs rely on rechargeable lithium-polymer (LiPo) batteries due to their high energy density and lightweight nature. The capacity and voltage of the battery pack determine the UAV’s flight endurance and performance, with larger batteries enabling longer flight times but also adding weight and reducing maneuverability.
Onboard Electronics
UAVs are equipped with a variety of onboard electronics, including sensors, cameras, communication systems, and data storage devices. These components enable the UAV to perform specific tasks such as capturing aerial imagery, collecting environmental data, or transmitting live video feeds. Advanced UAVs may also feature additional sensors for obstacle detection and avoidance, as well as payload systems for carrying cargo or scientific instruments.
Conclusion
From their sleek exteriors to their intricate inner workings, UAVs are marvels of modern engineering that continue to revolutionize industries and reshape the way we interact with the world around us. By understanding the key components that comprise these remarkable flying machines, we gain insight into the complexities and capabilities of UAV technology. Whether it’s capturing stunning aerial footage or conducting critical surveillance missions, the versatility and potential of UAVs are limited only by our imagination.