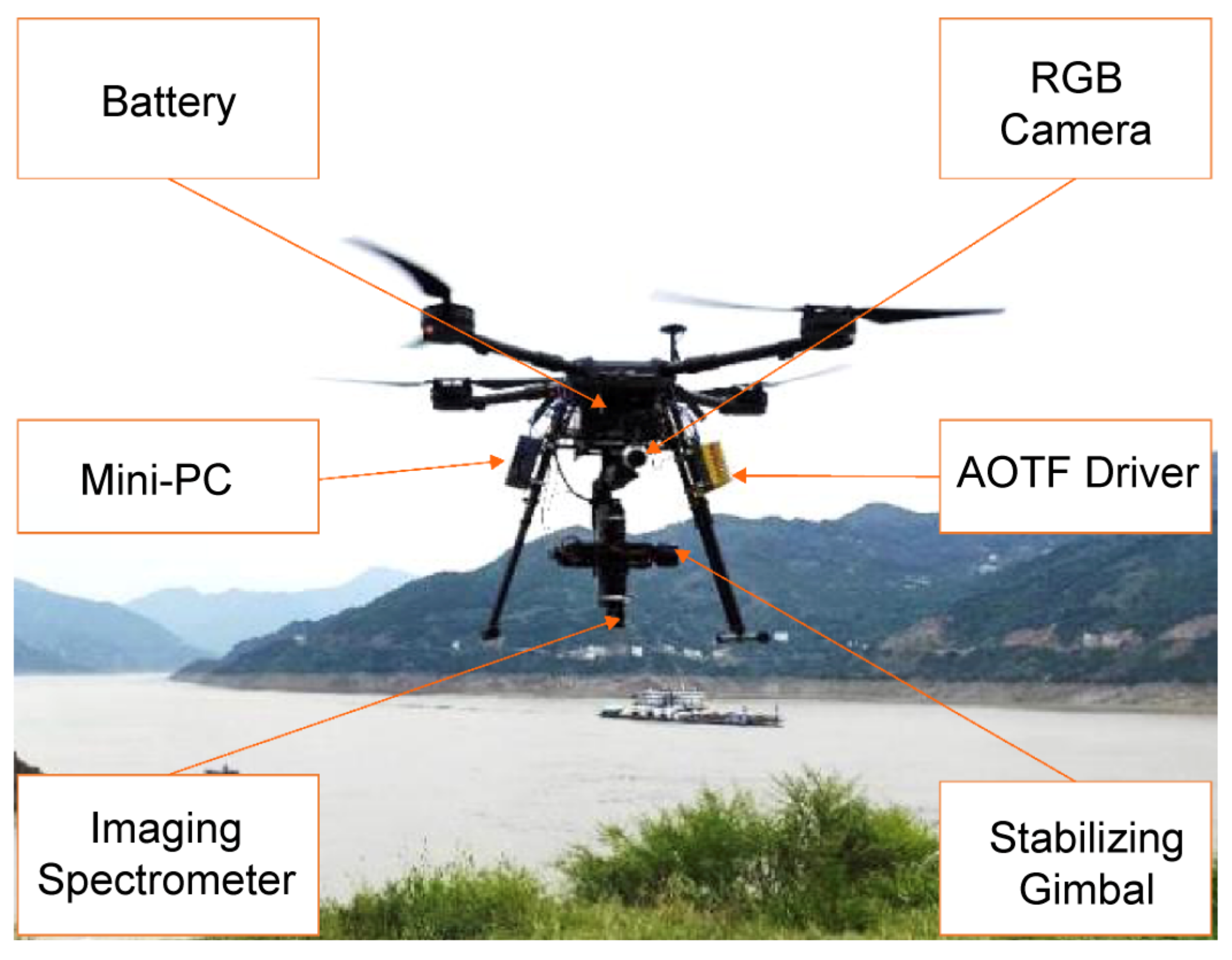
In the vast realm of technology, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), also known as drones, have emerged as versatile tools for various purposes, from capturing breathtaking aerial footage to aiding in search and rescue missions. At the heart of these flying marvels lies a sophisticated navigation system that enables them to soar through the skies with precision and efficiency.
Understanding UAV Navigation Systems
UAVs rely on a combination of advanced technologies to navigate through the air. These systems often include GPS (Global Positioning System), sensors, and sophisticated algorithms. GPS provides the drone with its exact location coordinates, similar to how it guides us when we use maps on our smartphones. However, drones also utilize additional sensors such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and magnetometers to maintain stability and orientation in flight.
Takeoff and Flight
Before takeoff, the UAV’s navigation system initializes, calibrating sensors and establishing a connection with GPS satellites. Once airborne, the system continuously collects data to ensure the drone stays on course. If it encounters any disturbances like strong winds or obstacles, the navigation system adjusts the drone’s flight path accordingly to maintain its trajectory.
Autonomous Navigation
Many modern UAVs boast autonomous navigation capabilities, meaning they can operate without constant manual control. Through pre-programmed waypoints or real-time decision-making algorithms, these drones can navigate complex routes and perform tasks with minimal human intervention. This autonomy is particularly valuable in applications like aerial surveys, agriculture, and infrastructure inspection, where efficiency and accuracy are paramount.
Challenges and Innovations
While UAV navigation systems have come a long way, challenges persist, especially in environments with poor GPS reception or dense urban areas with numerous obstacles. To overcome these hurdles, researchers and engineers are continuously developing innovative solutions. This includes integrating artificial intelligence for better decision-making, enhancing sensor technology for improved accuracy, and exploring alternative navigation methods such as visual odometry and LiDAR.
Future Prospects
As technology evolves, the capabilities of UAV navigation systems are expected to expand even further. We may witness drones seamlessly navigating indoor environments, collaborating in swarms for collective tasks, or even delivering goods autonomously in urban settings. With each advancement, UAVs are becoming indispensable tools in various industries, revolutionizing how we perceive and interact with the world from above.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the navigation systems of UAVs represent a remarkable fusion of technology and innovation. From their humble beginnings to their current state of sophistication, these systems continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in aerial exploration and beyond. As we look to the future, the skies are truly the limit for the capabilities of unmanned aerial vehicles.